Scientific Images

von Willebrand Factor (VWF) Is not required for red blood cell retention in clots in mice (View publication)
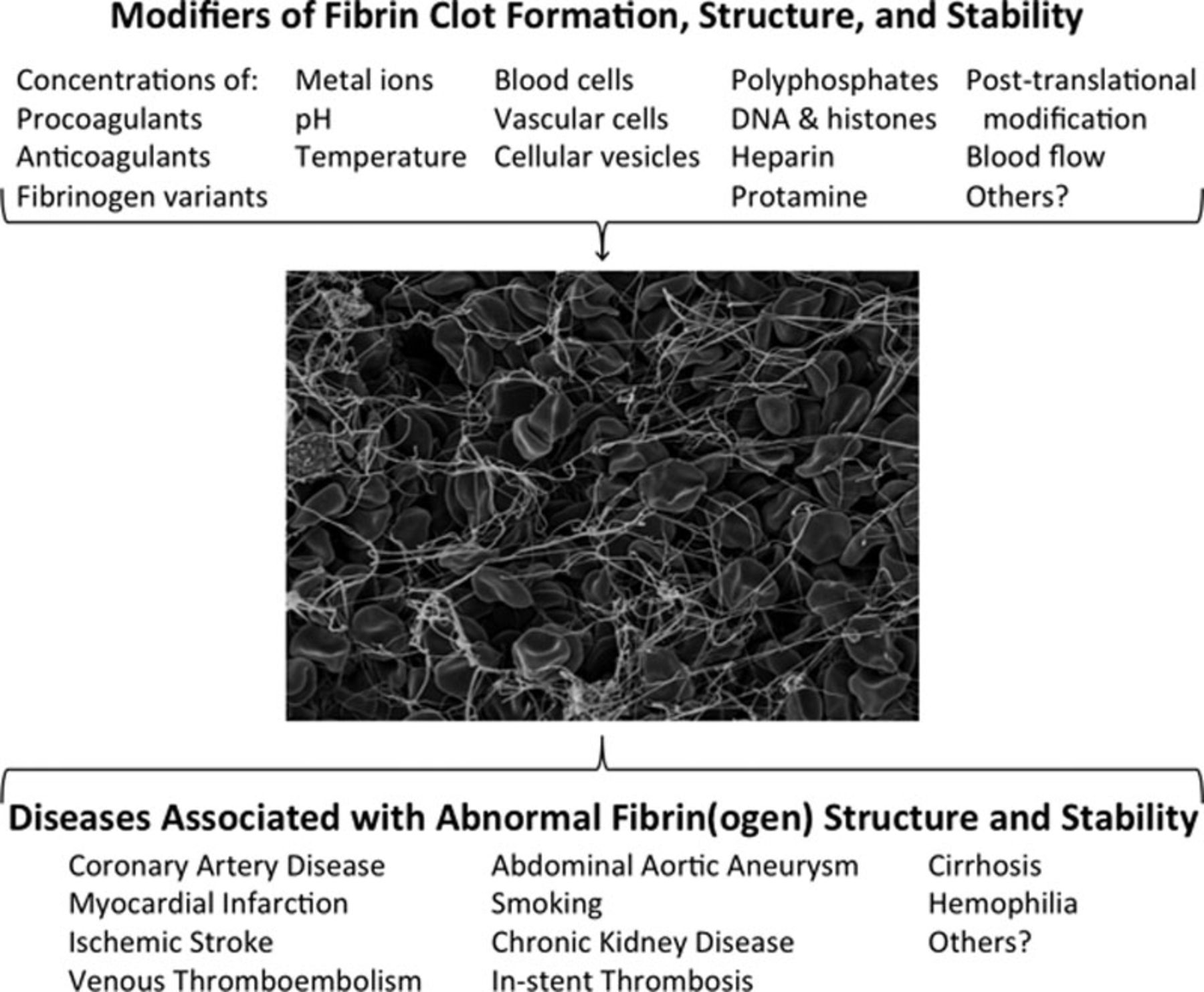
Modifiers of fibrin(ogen) and association with disease (View publication)
![FXIIIa cross-linking during fibrin formation FXIIIa cross-linking during fibrin formation. Fibrinogen is a hexamer composed of 2 Aα- (purple), 2 Bβ- (blue), and 2 γ-chains (green). During coagulation, thrombin cleaves N-terminal fibrinopeptides from the Aα- and Bβ-chains, producing fibrin monomers which polymerize into protofibrils and subsequently, fibers. FXIIIa increases clot stability by introducing ε-N-(γ-glutamyl)-lysyl cross-links between residues in the γ- and α-chains of fibrin monomers within individual fibers. FXIIIa first introduces cross-links between γ-chains (forming γ-γ dimers) and subsequently between γ- and α-chains (forming high-molecular-weight species [γ-multimers, α-polymers, and αγ-hybrids]).](https://www.med.unc.edu/wolberglab/wp-content/uploads/sites/645/2018/04/fxiiia-cross-linking-during-fibrin-formation.jpeg)
FXIIIa cross-linking during fibrin formation (View publication)
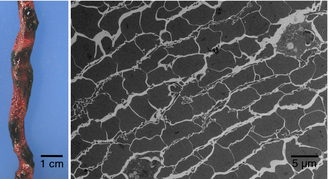
Venous thrombi contain regions of high RBC and fibrin content (View publication)
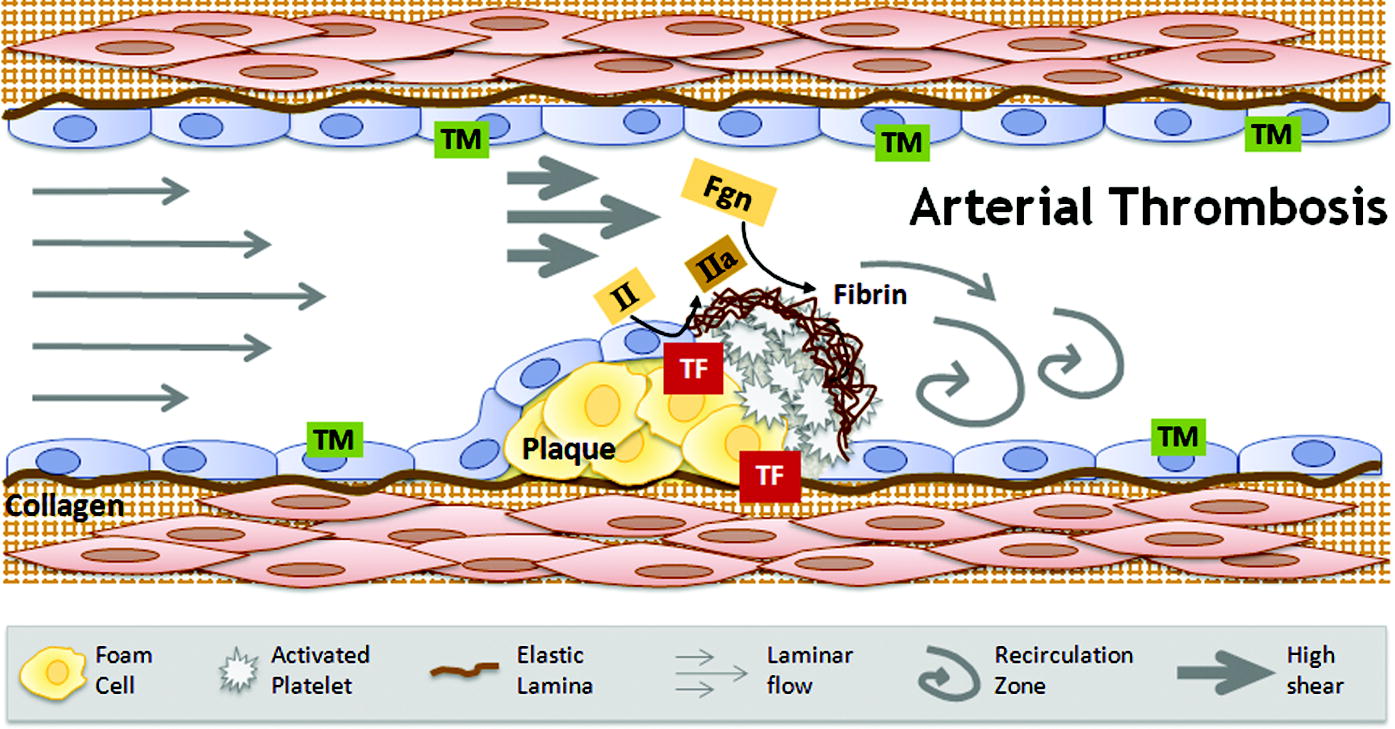
Arterial thrombosis. Abbreviations: TM, thrombomodulin; II, prothrombin; IIa, thrombin; Fgn, fibrinogen; TF, tissue factor (View publication)
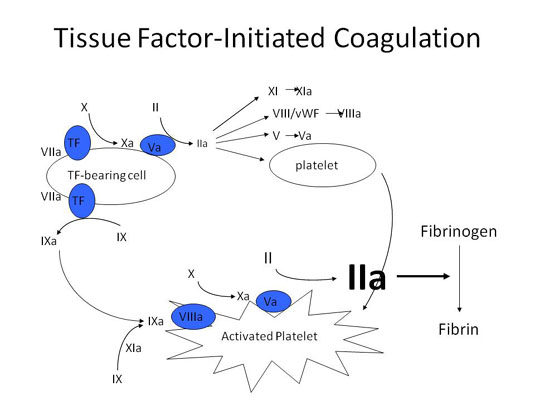
Schematic of cell-mediated procoagulant activities leading to fibrin clot formation
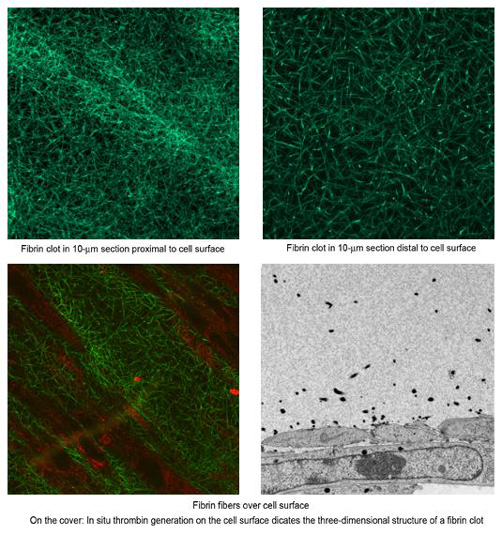
Distribution of fibrin fibers above a cell surface (Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscopy)
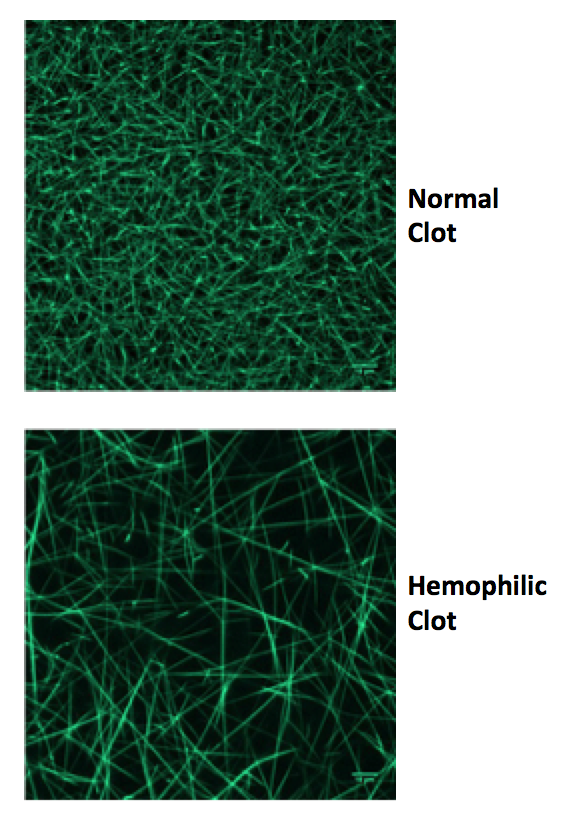
Confocal micrographs of normal vs. hemophilic clots (View publication)
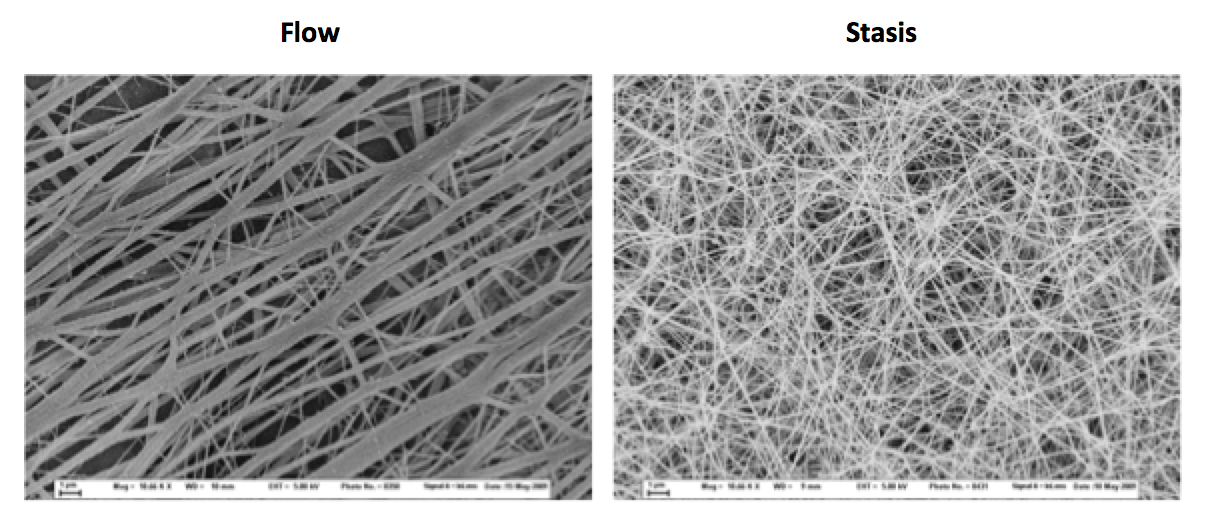
Scanning electron micrographs of networks formed under flow (left) and stasis (right) (View publication)
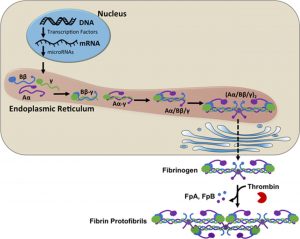
Fibrinogen synthesis and expression (View publication)
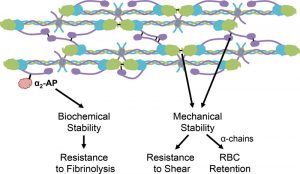
Contributions of FXIIIa to clot stability (View publication)
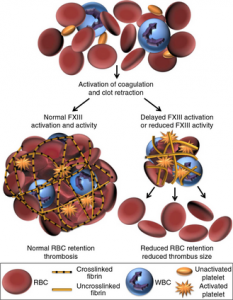
FXIIIa mediates RBC retention in thrombi (View publication)
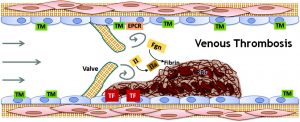
Venous thrombosis. Abbreviations: TM, thrombomodulin; EPCR, endothelial protein C receptor; II, prothrombin; IIa, thrombin; TF, tissue factor; Fgn, fibrinogen; RBC, red blood cells (View publication)
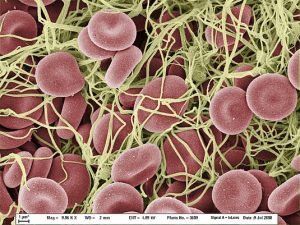
Scanning electron micrograph of a whole blood clot
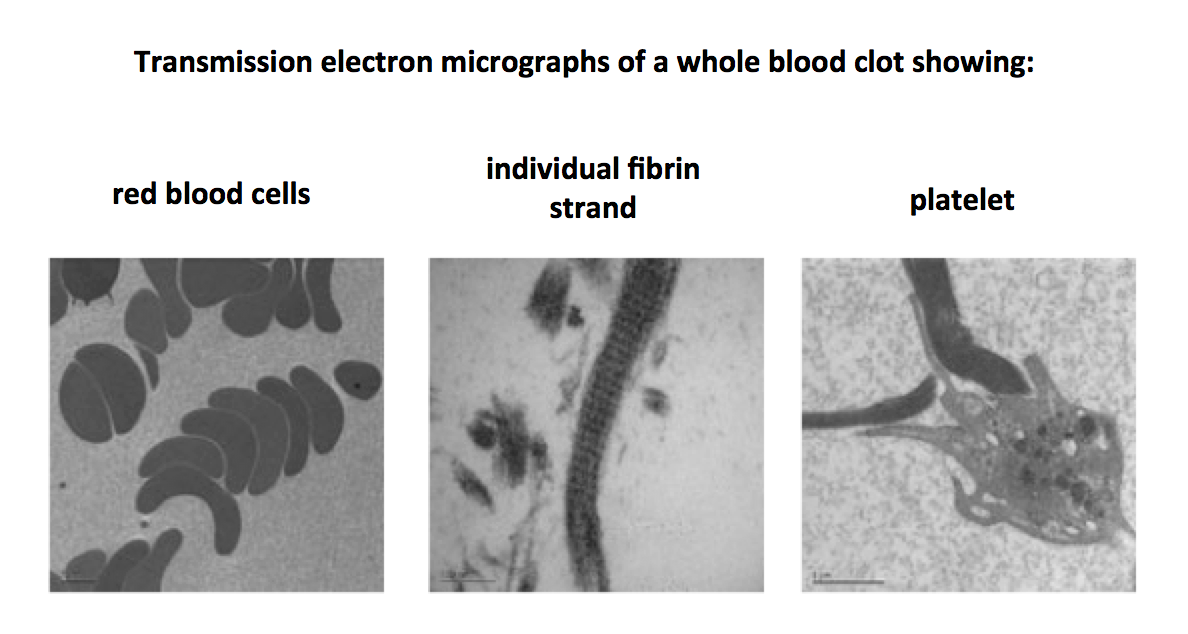
Transmission electron micrographs of a whole blood clot
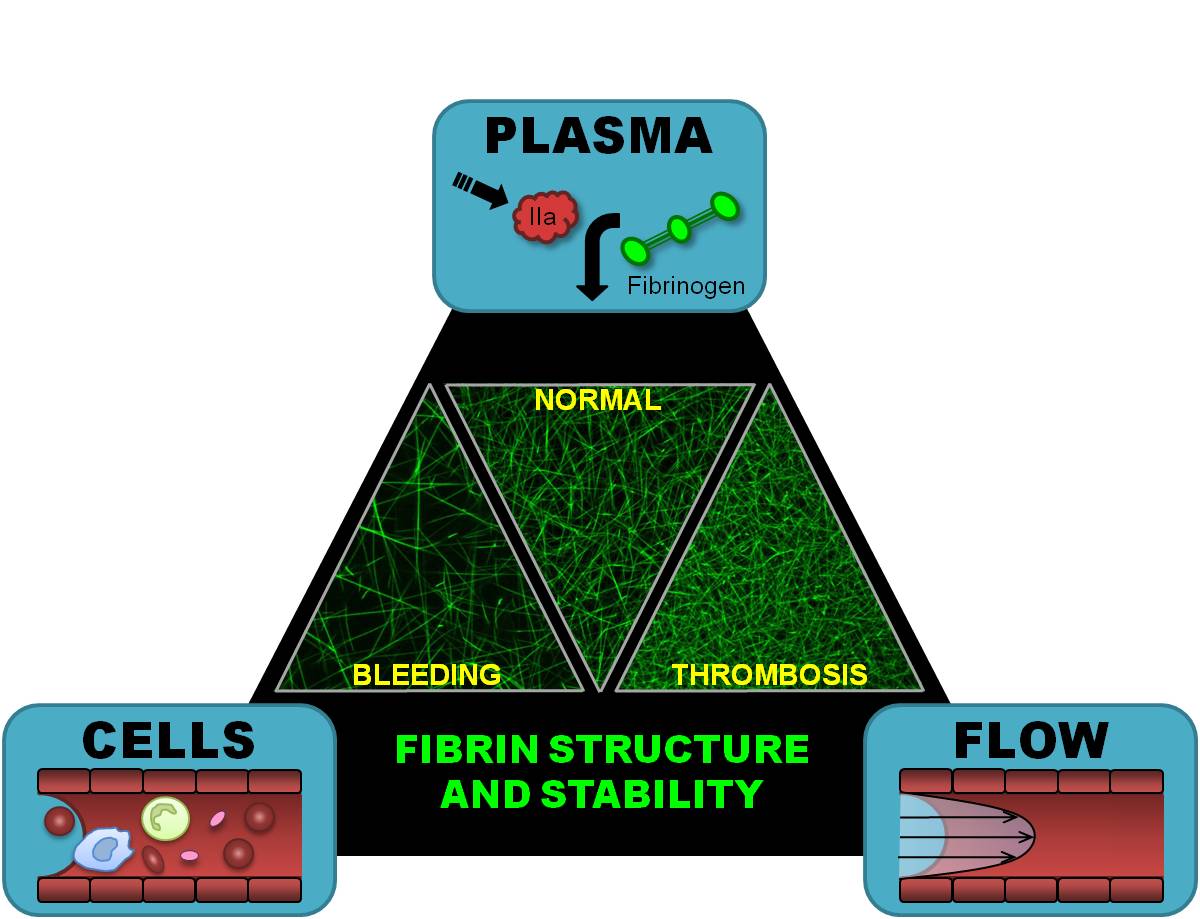
Virchow’s Triad (View publication)
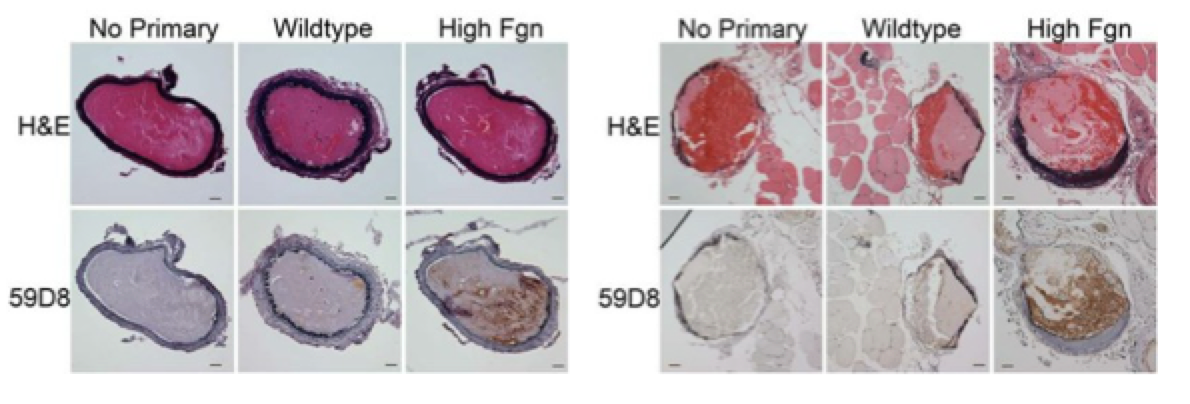
Effects of elevated fibrinogen on thrombus development in carotid artery (left) and saphenous vein (right)
(View publication)